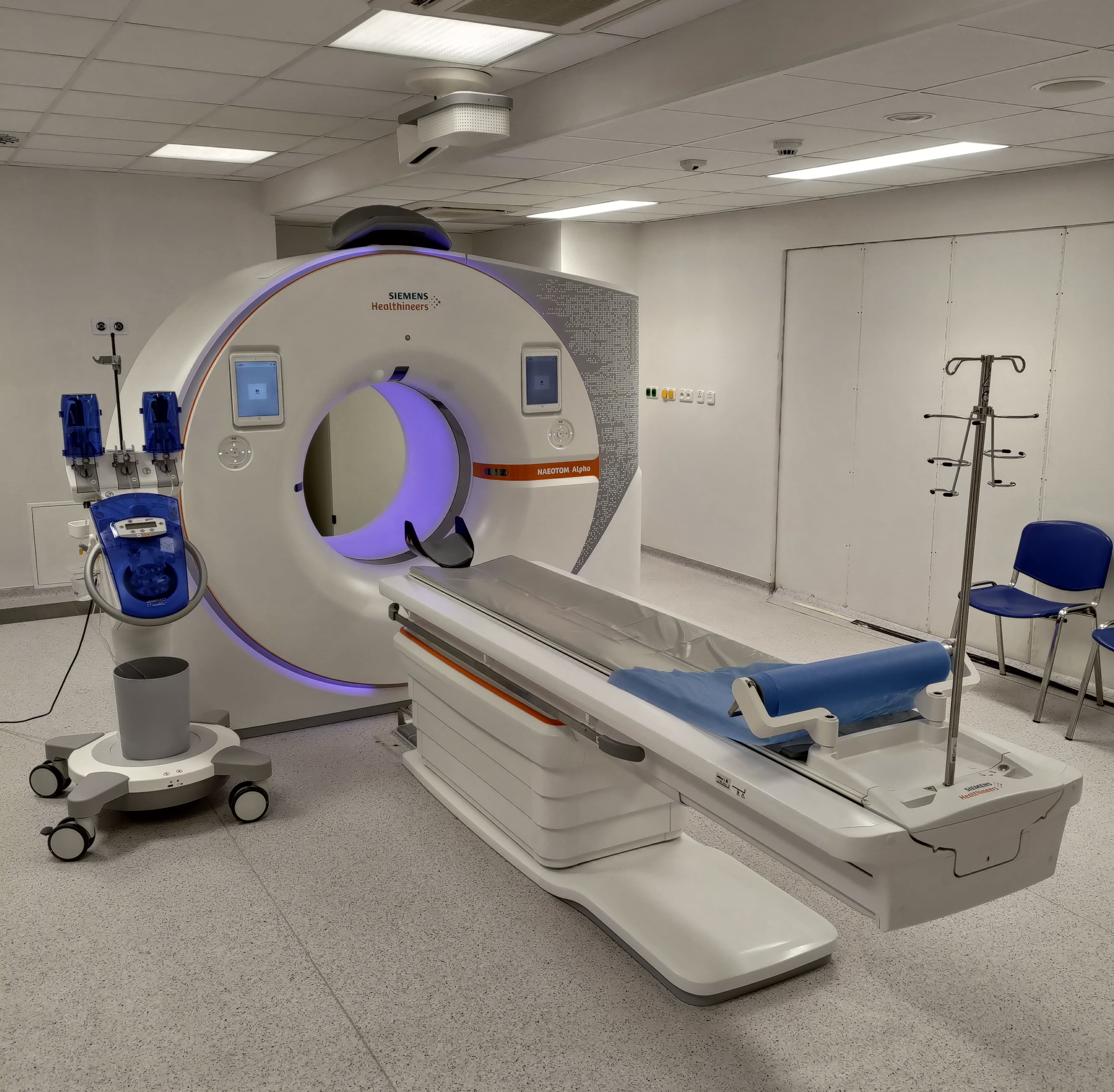
CT scan services in hospitals are essential for diagnosing various medical conditions by providing detailed images of the body's internal structures. Here’s an overview of what CT scan services typically involve:
1. What is a CT Scan?
- Definition: A Computed Tomography (CT) scan combines X-ray images taken from different angles and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of bones, organs, and tissues.
- Uses: CT scans are used to diagnose conditions such as tumors, internal injuries, infections, and diseases of the brain, chest, abdomen, and pelvis.
2. CT Scan Procedure
-
Preparation:
- Patients may need to avoid food or drink for a few hours before the scan.
- Certain medications or allergies (especially to contrast material) should be discussed with the medical team.
-
During the Scan:
- Patients lie on a table that slides into the CT machine.
- The machine takes multiple X-ray images from different angles.
- If a contrast dye is used (often injected or ingested), it helps enhance the images.
-
Duration: The scan typically lasts 10 to 30 minutes, depending on the area being examined.
3. Types of CT Scans
- CT Angiography: Used to visualize blood vessels and blood flow.
- CT Colonography: Specifically for examining the colon.
- High-Resolution CT: Often used for lung assessments.
4. Safety and Risks
- Radiation Exposure: CT scans involve exposure to radiation, but the benefits often outweigh the risks when used appropriately.
- Allergic Reactions: Some patients may have allergic reactions to contrast material, although serious reactions are rare.
5. Interpreting Results
- Radiologists: The images are reviewed by radiologists who provide a report to the referring physician.
- Follow-Up: Based on the results, further tests or treatments may be recommended.
6. Advancements in CT Technology
- 3D Imaging: Newer CT machines can create three-dimensional images, aiding in more accurate diagnoses.
- Lower Radiation: Advances in technology have also led to lower radiation doses for patients.
7. Accessibility
- Hospital Services: Most hospitals have dedicated radiology departments that offer CT scan services, often available 24/7 for emergencies.
- Outpatient Centers: Some outpatient facilities also provide CT scans for non-emergency situations.