ECG (electrocardiogram) services are essential for assessing heart health by measuring the electrical activity of the heart. Here’s an overview of what ECG services typically involve:
1. ECG
- An ECG is a test that records the electrical signals of the heart over a period of time, providing information about its rhythm and function.
- Commonly used to diagnose arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac conditions.
2. Types of ECG
- Standard ECG: A 12-lead ECG is the most common type, capturing detailed information about the heart's electrical activity.
- Holter Monitor: A portable ECG device worn for 24 to 48 hours to record heart activity continuously during daily activities.
- Event Monitor: Similar to a Holter monitor but used for longer periods; patients activate it to record data when they experience symptoms.
- Stress Test ECG: Conducted during exercise (often on a treadmill) to evaluate heart function under stress.
3. ECG Procedure
-
Preparation:
- No special preparation is usually required for a standard ECG, but patients may be asked to avoid caffeine or stimulants beforehand.
- For Holter or event monitors, patients may receive specific instructions on when to activate the device.
-
During the ECG:
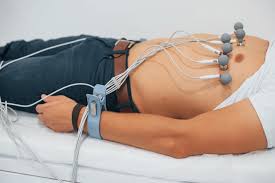
- Standard ECG: Electrodes are placed on the chest, arms, and legs. The patient typically lies down and remains still for a few minutes while the test is performed.
- Holter/Event Monitor: Patients wear the device for a specified time, and it records heart activity as they go about their normal routines.
-
Duration: A standard ECG takes about 5 to 10 minutes, while Holter monitors are worn for a day or more.
4. Interpreting Results
- Analysis: A trained healthcare professional, often a cardiologist, interprets the ECG results to identify any abnormalities.
- Follow-Up: Based on the findings, further testing or treatment may be recommended.
5. Safety and Risks
- Non-Invasive: ECGs are safe and non-invasive, with no associated risks.
- Discomfort: Some patients may experience minor skin irritation from the electrodes.
6. Advancements in ECG Technology
- Portable Devices: Newer, compact ECG devices allow for at-home monitoring and telehealth consultations.
- Mobile Health Applications: Some smartphones can perform ECGs using attached devices or built-in technology.
7. Accessibility
- Hospital Services: ECG services are available in hospitals, clinics, and outpatient facilities.
- Emergency Situations: ECGs are often performed in emergency departments to assess patients with chest pain or other cardiac symptoms.